Industrial ovens are thermal processing machines that provide various applications with the very important process of heat treatment. During this process, heat speeds up the molecular activity inside an object. Inside solid objects, molecules are arranged in lattices that vibrate from the heat, while in gases, these molecules collide. This activity changes the properties of the object it is heating, and strengthens it. Read More…
Weiss Envirotronics is a worldwide leader in the design, manufacturer and service of environmental test chambers. A complete line of standard and custom chambers, from bench top models to full walk-in and drive-in solutions to meet any testing requirement. Not sure what you need? Let one of our applications engineers help. Weiss Envirotronics, Inc is ISO 9001 registered and A2LA accredited.

Complete finishing systems are designed around your specific process needs and are optimized to fit within your space requirements. We specialize in producing paint systems for wet and powder coatings, while also providing comprehensive design, fabrication, installation, start-up, and training services. Our complete finishing systems consist of an overhead conveyor, pretreatment washer, dry-off...

Surface Combustion offers a diverse product offering for batch, continuous furnace designs for atmosphere, non-atmosphere, or vacuum processing of ferrous and/or nonferrous components/materials. The convection design is optimal for temperatures between 350°F – 1400°F and are engineered to perform and built to last.
Belco Industries is a leading supplier of high-quality finishing systems, including industrial ovens: batch ovens, moisture drying ovens, infrared preheat, dewatering, E-coat cure ovens, powder coat cure ovens, paint bake ovens and more. We attribute our success to our diversified product line and our ability to change with the demands of the modern industrial market. Call today for more...
Pyromaitre specializes in industrial ovens and furnaces, and have been providing quality equipment for the past 30 years. Our industrial ovens and furnaces have a compact layout, and are designed with energy efficiency and maximum productivity in mind. We also offer customization options if you are unable to find the exact oven you are looking for. For more information, contact Pyromaitre today!
MFS offers superior dry off industrial ovens & curing ovens for all your powder coating needs. Our modular oven design means quick install & start up. As a manufacturer of highly energy efficient ovens, we customize design, engineering, fabrication & installation to maximize your production potential. Dedicated to meeting your needs, we can do complete coating, curing, washing & dry off systems.
More Industrial Oven Manufacturers
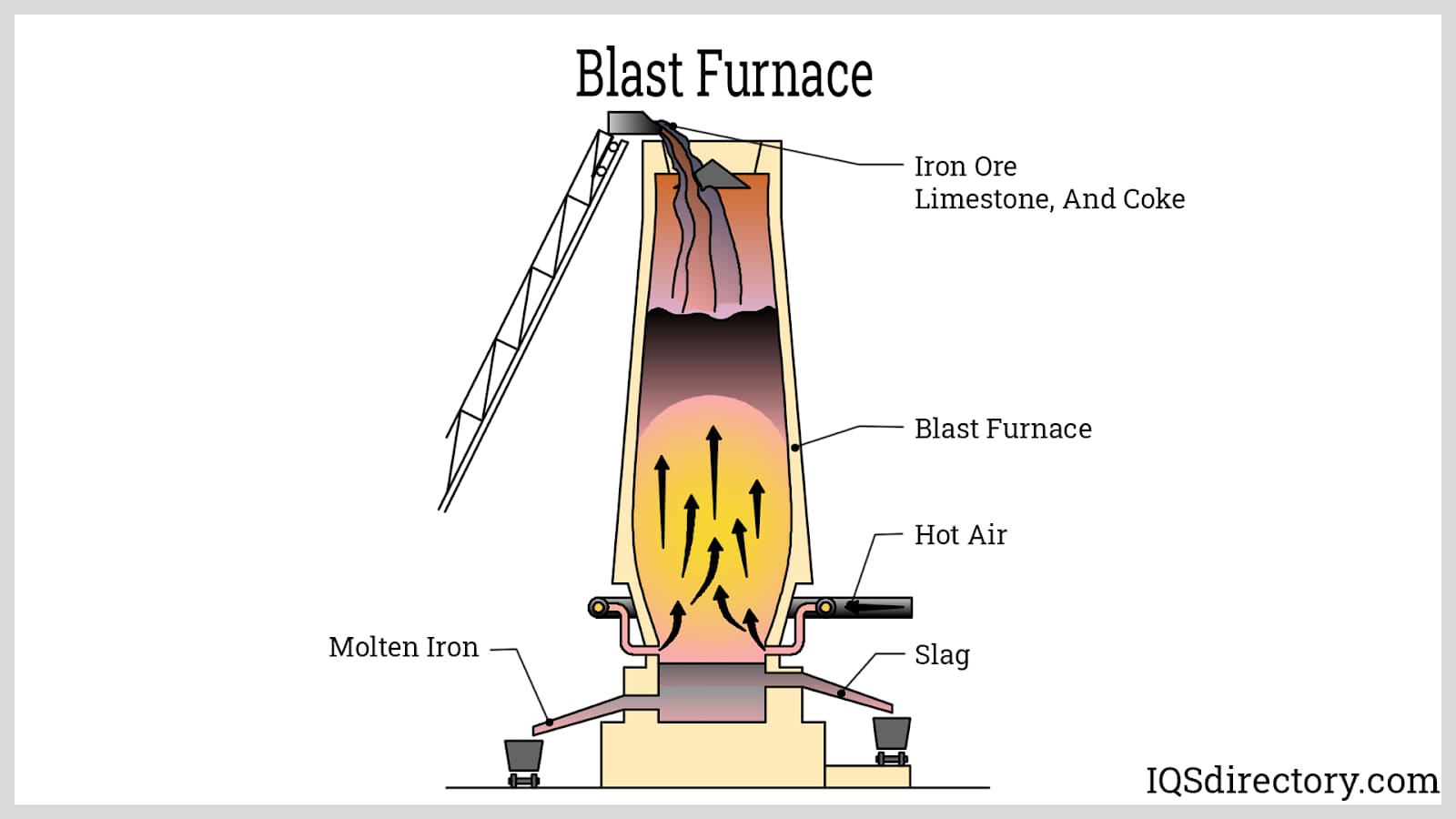
Please note: Industrial ovens serve distinct purposes from furnaces. Furnaces can achieve much higher temperatures (exceeding 2000℉) and are typically larger in size. It’s common for industrial manufacturers to also specialize in furnace production.
Applications
Industrial ovens find extensive use across diverse industries including manufacturing, electronics, food and beverage production, healthcare and medicine, pharmaceuticals, chemical processing, research and development, plastics manufacturing, aerospace technology, automotive industry, and metal forming.
Industrial ovens play a pivotal role in enhancing the strength of metal products, ensuring hygienic conditions in healthcare facilities, and expanding the versatility of extruded polymer goods. They are indispensable in treating a wide array of products such as steel coils, automotive components, tubing, electronics, construction materials, fuel cells, carpets, and textiles. Moreover, laboratories utilize these ovens to deepen their understanding and improve industrial heat transfer processes (known as laboratory ovens). This research drives advancements in reducing inefficiencies in heat transfer and pioneering new applications for heat treatment.
These processes serve specific functions: sintering, curing, and powder coating. Sintering involves heating fine particles to fuse them into larger ones without melting. Curing solidifies materials by subjecting them to consistent heat and dry conditions. During powder coating, a product is placed in an oven for two to 10 minutes, where the powder melts and forms a smooth coating, aided by convection or infrared heat. Ultraviolet light then briefly cures and hardens the finish while the product remains in the oven.
History
Since as early as 2900 BC in Central Europe, ovens have played a crucial role. Initially, they were simple pits used for boiling and roasting mammoths within nomadic yurts. These primitive ovens soon evolved, with people employing hot coals buried under ashes for more efficient cooking. Within just three centuries, hearths became widespread across settlements, serving dual purposes of cooking and brick-making.
The hearth-style brick ovens eventually transformed into kilns, a concept introduced by the Greeks, which were utilized not only for baking bread but also for pottery. As time progressed, ceramic and earth ovens were phased out in favor of fireplaces and cauldrons, marking a significant shift in culinary technology. Over subsequent centuries, ovens adapted to various energy sources, from coal and wood to iron gas, and eventually, electricity.
During the Industrial Revolution, industrial ovens saw a transformative breakthrough. In the 1700s, Philo Penfield Stewart introduced the Stewart Oberlin iron oven, marking a shift towards smaller, more ventilated designs. By the early 1800s, coal ovens were being manufactured, followed by James Sharp’s pioneering gas oven patent in 1826. Gustaf Dalen further innovated in 1922 with the AGA cooker, and Percy Spencer revolutionized kitchens in 1946 with the compact yet groundbreaking microwave oven. Today, high-tech ovens, including microwaves, cater to diverse applications, ranging from compact designs to large-scale models.
How It Works
Industrial ovens harness heat and mass transfer through radiant infrared heat, conduction, convection, or a blend of these methods.
In industrial ovens, infrared radiation stands out as the most efficient method for transferring heat. Conversely, natural convection ranks as the simplest among these methods. Gravity initiates fluid movement, causing heated molecules to rise and cooler ones to descend. This circulation facilitates heat transfer through gasses and liquids. Typical gasses employed are natural gas and propane. Conduction, less favored, involves heat transferring initially to air within the oven, which then heats solid objects, spreading throughout them. Although alternative methods exist, they prove less efficient and are seldom utilized.
Types
Infrared Oven
Infrared ovens utilize electromagnetic radiation for heat transfer. By bypassing the need to heat the air within the enclosure, these ovens directly apply electromagnetic waves emitted from a tungsten coil onto the product.
Convection Oven
Convection ovens employ either an electrified coil or a gas-fired heating element to ensure uniform internal heating. This method is ideal for smaller quantities; however, larger batches may experience uneven heat distribution unless the oven is equipped with a fan to enhance air circulation and overcome this challenge. Commercial convection ovens are commonly utilized in extensive baking operations.
Batch Oven
Industrial batch ovens come in diverse sizes, from compact and mobile units to expansive fixtures that occupy entire rooms permanently. These ovens specialize in processing materials in discrete batches, making them favored by large-scale commercial manufacturers handling substantial product volumes, as well as by smaller industrial heat treaters who value their precise and uniform heat distribution. Referred to interchangeably as cabinet ovens or walk-in ovens, batch ovens support various processes such as curing, drying, annealing, and aging.
Vacuum Oven
Some batch ovens are designed to release the enclosed atmosphere, preventing heat-treated metals from suffering surface oxidation. These specialized ovens are known as vacuum ovens.
Continuous Oven
Continuous ovens, in contrast to batch ovens, excel in multitasking. With dedicated warming and cooling stations, they accelerate thermal processes more efficiently than their counterparts. Ideal for large-scale operations demanding uniform heat treatment.
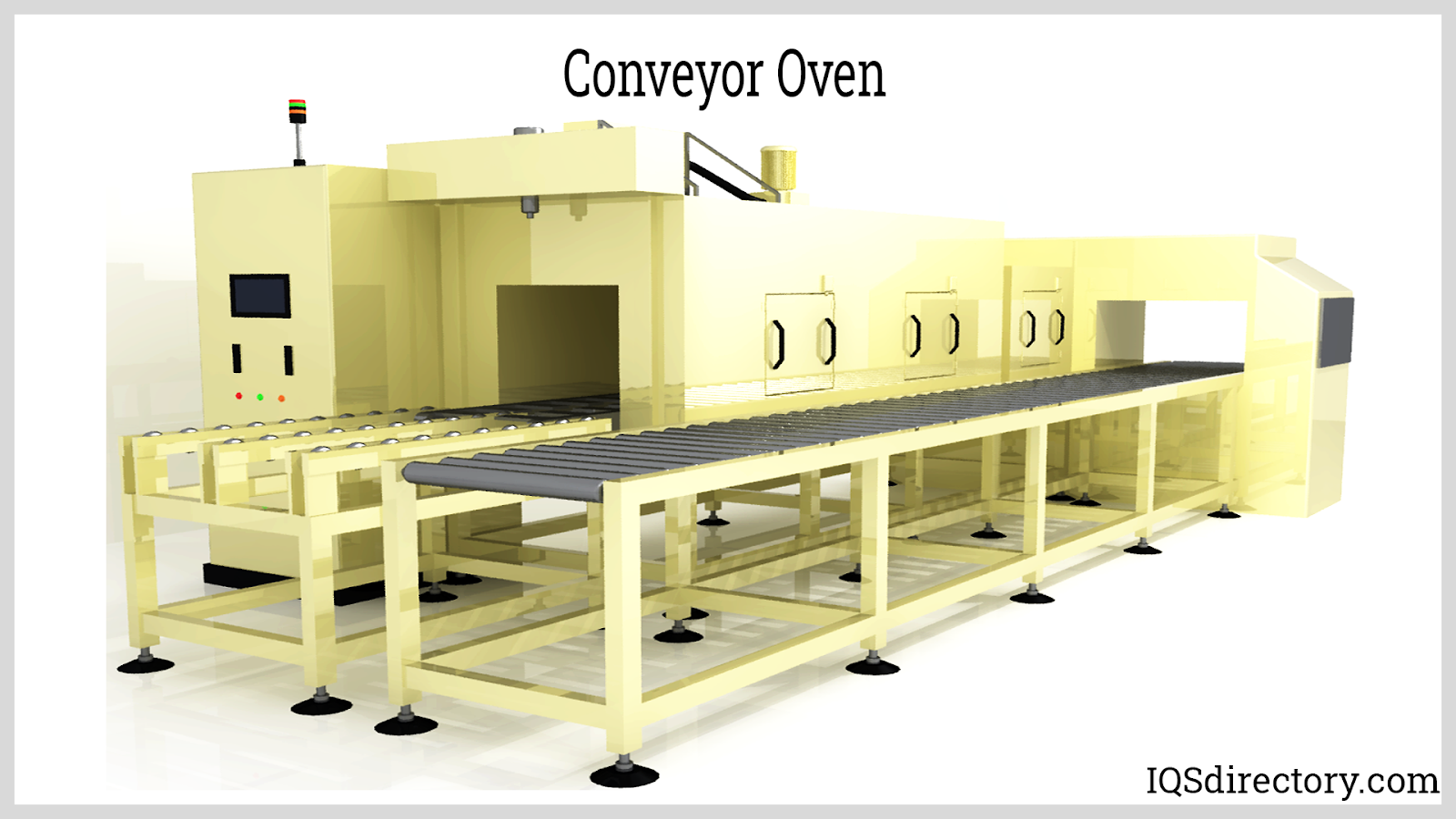
Conveyor Oven
Conveyor ovens, designed to shuttle products through a heated chamber via automated conveyor belts, typically find utility primarily in large-scale operations. Their cost-effectiveness hinges on a consistent flow of products to justify their operation.
In contrast, batch and continuous ovens, though distinct in operation, can each fulfill roles such as sintering, robust powder coating, drying, or curing applications.
Drying Oven
Drying ovens efficiently extract moisture from raw materials using a structured three-step process. First, in the heat-up phase, substances reach their optimal temperature within the oven. Next, during the soak phase, materials absorb this heat for a specified duration. Lastly, in the cool-down stage, hot air exits while cooler air replaces it. Drying ovens excel in tasks like sterilization, incubating temperature-sensitive experiments, and conducting temperature tests.
Tunnel Oven
Tunnel ovens are cylindrical appliances designed to heat raw materials as they travel through their length. These materials can be fed into the oven either continuously or in batches using a conveyor belt. Tunnel ovens generate heat from various fuel sources, working in tandem with the belt’s speed. Ideal for cooking, these ovens are especially suited for preparing meat and baked goods.
Burn-off Oven
Burn-off ovens, also called heat-cleaning ovens, purify objects by incinerating contaminants and coatings. These ovens effectively remove substances such as varnish, paint, grease, epoxy, oil, and bonded rubber. They are particularly useful for cleaning and decoating automobiles and various machinery.
Equipment Components
Every custom oven is unique, yet most industrial ovens typically share these key components: a motor that drives the system, a duct network for ventilation, fans for exhaust and recirculation, purge timers, flame controllers, and burners.
How to Use It
Each model of oven is unique, so we can’t provide exact instructions for yours. However, we can offer some general guidelines. First, let’s talk about installation. Choosing the right spot for your oven is crucial. The location should protect it from high temperatures, mechanical damage, vibrations, and other hazards. Avoid placing your oven directly against the wall. If your cabinet is made of stainless steel, which is common, you’ll need to level it with a shim. This shim helps support the oven as it expands during use (stainless steel expands when heated). Additionally, ensure that your installation site has adequate ventilation. Finally, make sure you follow all relevant standards, specifications, and codes when installing and using your oven.
If you’re unsure about installing your industrial oven, don’t hesitate to contact your supplier for guidance or professional installation assistance.
Benefits
There are many reasons to love industrial ovens. These include: air flow efficiency, speed, durability, consistency, easy temperature management and cost effectiveness.
Air Flow Efficiency
Air flow efficiency ensures that the heat is evenly distributed throughout any device you place in the oven. Uniform air temperature guarantees consistent heating performance, which is a crucial aspect of most machine operations.
Speed
Industrial ovens swiftly produce heat waves while conserving energy, enabling manufacturers to accomplish numerous tasks in a short span of time.
Durability and Consistency
Constructed predominantly from stainless steel, most industrial ovens boast exceptional durability, reliability, and performance.
Temperature Management
Industrial ovens offer effortless temperature control and significantly reduce the risk of uneven heat distribution.
Cost Effectiveness
Though prices vary, acquiring an industrial oven is relatively affordable. Moreover, their reliability makes them outstanding investments.
Design and Customization
Crafting an industrial oven involves taking numerous factors into account. Initially, manufacturers assess its intended use. Is the oven for food production, requiring food-grade standards, or is it meant for processing equipment? These specific applications dictate the oven’s functionality, power source (whether gas or electric), and temperature specifications. If desired, manufacturers can tailor the oven to meet your unique requirements.
Safety and Compliance Standards
Due to their operations involving heat, gas, and more, ensuring your industrial oven meets safety standards is crucial. In the USA, the NFPA (National Fire Protection Association) sets key benchmarks for this purpose. These specifications guide both manufacturers and users of industrial ovens on safe practices during construction, installation, and operation, minimizing potential hazards.
Here are some safety tips to ensure your well-being at all times:
- Always wear appropriate protective gear to prevent direct inhalation of gases and contact with hot surfaces or electrical components.
- Ensure that heating compartments are tightly sealed to prevent spills from spreading easily.
- Use ducts constructed from non-combustible materials.
- Conduct regular inspections of ovens in line with safety standards and manufacturer guidelines.
- Keep moving parts adequately lubricated on a routine basis.
- Never leave an oven unattended for any reason.
Things to Consider
Finding the right manufacturer can be a daunting task. Begin by compiling a list of trusted sources. Right here, just a scroll away, you’ve completed the first step! We’ve done the legwork to identify top-tier industrial oven companies with extensive experience and a solid reputation. Their profiles are conveniently listed on this page. Take the time to explore their offerings and websites. Look for companies that align with your specific requirements. Select three or four that pique your interest and reach out to each with your project details. During your discussions, ensure they provide essential services such as standard certifications, factory testing, troubleshooting, delivery, installation, and post-installation support. Once you’ve identified your ideal match, reach out again via phone or email to kickstart your project.
Check out our Environmental Test Chambers website





 Electric Heaters
Electric Heaters Industrial Dryers
Industrial Dryers Industrial Mixers
Industrial Mixers Industrial Ovens
Industrial Ovens Pressure Vessels
Pressure Vessels Pulverizers
Pulverizers Vibratory Feeders
Vibratory Feeders AGV
AGV Air Pollution Control
Air Pollution Control Assembly Machinery
Assembly Machinery Blowers
Blowers Conveyors
Conveyors Cranes
Cranes Deburring Machinery
Deburring Machinery Dust Collectors
Dust Collectors Heaters
Heaters Hose Reels
Hose Reels Lubricators
Lubricators Mezzanines
Mezzanines Modular Buildings
Modular Buildings Storage Racks
Storage Racks Ultrasonic Cleaners
Ultrasonic Cleaners Work Benches
Work Benches